Hammertoe Correction
 Overview
Overview
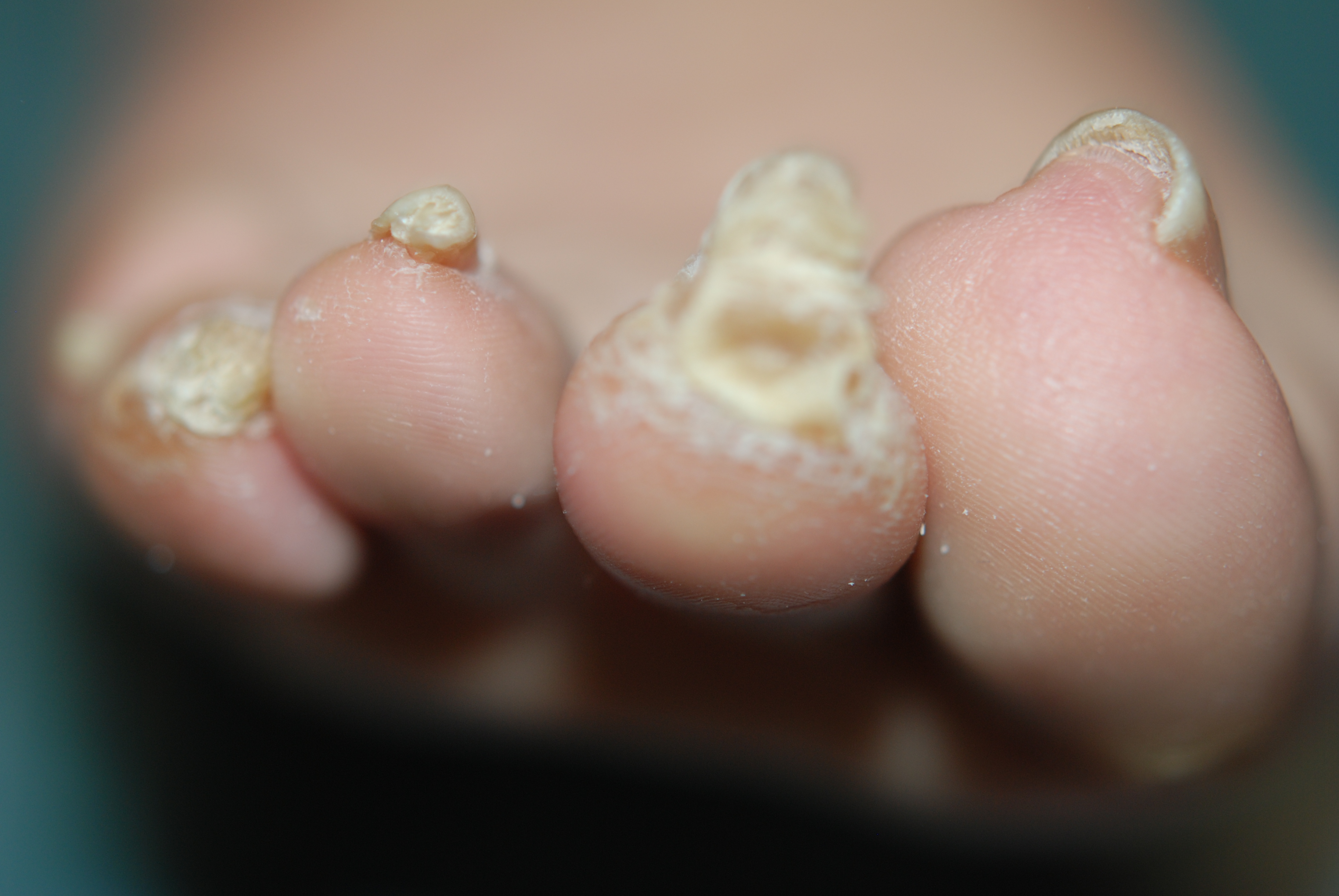
What are hammertoes, mallet toes and claw toes? Often the words are used interchangeably to mean an abnormally contracted toe like the drawing above. Technically speaking, a "hammertoe" is the name for a toe that is contracted at the first toe joint. If it's contracted at the second toe joint it is called a "mallet toe". IIf a toe is contracted at both toe joints, it is called a "claw toe". Each of these conditions can be quite uncomfortable and are cosmetically unappealing.
Causes
Hammertoe has three main culprits: tight shoes, trauma, and nerve injuries or disorders. When toes are crowded in shoes that are too tight and narrow, they are unable to rest flat, and this curled toe position may become permanent even when you aren't wearing shoes due to the Hammer toe tendons of the toe permanently tightening. When the tendons are held in one position for too long, the muscles tighten and eventually become unable to stretch back out. A similar situation may result when tendons are injured due to trauma, such as a stubbed, jammed, or broken toe.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Well-developed hammertoes are distinctive due to the abnormal bent shape of the toe. However, there are many other common symptoms. Some symptoms may be present before the toe becomes overly bent or fixed in the contracted position. Often, before the toe becomes permanently contracted, there will be pain or irritation over the top of the toe, particularly over the joint. The symptoms are pronounced while wearing shoes due to the top of the toe rubbing against the upper portion of the shoe. Often, there is a significant amount of friction between the toe and the shoe or between the toe and the toes on either side of it. The corns may be soft or hard, depending on their location and age. The affected toe may also appear red with irritated skin. In more severe cases, blisters or open sores may form. Those with diabetes should take extra care if they develop any of these symptoms, as they could lead to further complications.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe.
Non Surgical Treatment
Inserts in your shoes can be used to help relieve pressure on the toes from the deformity. Splints/Straps. These can be used to help re-align and stretch your toes and correct the muscle imbalance and tendon shortening. One of the most common types are toe stretchers like the yogatoe. Chiropody. A chiropodist can remove calluses or corns, areas of hard skin that have formed to make the foot more comfortable.Steroid injections can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes surgery can not be avoided. If needed, the surgery chosen is decided by whether we are dealing with a flexible or rigid hammer toe. If the surgery is on a flexible hammer toe, it is performed on soft tissue structures like the tendon and or capsule of the flexor hammer toe. Rigid hammer toes need bone surgeries into the joint of the toe to repair it. This bone surgery is called an arthroplasty.
 Prevention
Prevention
To help prevent hammer toes from developing, wear shoes or boots that provide sufficient width in the toe box to ensure minimal compression. Use inserts that help the toes flatten out and spread and give sufficient support to the metatarsal arch in the forefoot. If hammer toes have already formed, padded socks help protect the tops and the tips of the hammer toes and may reduce pain from rubbing and chafing.
All The Things You Want To Find Out On The Subject Of Bunions
Overview
 A bunion is an abnormal bump, or bony enlargement that forms at the base of your big toe. In the early stages, the bunion may be small and the side of your foot may be slightly swollen. As it progresses, the bump gets larger and becomes increasingly painful. Your big toe may point towards your other toes, rather than straight. Shoes may be uncomfortable to wear and add to the irritation of the joint.
A bunion is an abnormal bump, or bony enlargement that forms at the base of your big toe. In the early stages, the bunion may be small and the side of your foot may be slightly swollen. As it progresses, the bump gets larger and becomes increasingly painful. Your big toe may point towards your other toes, rather than straight. Shoes may be uncomfortable to wear and add to the irritation of the joint.
Causes
The classic bunion, medically known as hallux abductovalgus or HAV, is a bump on the side of the great toe joint. This bump represents an actual deviation of the 1st metatarsal and often an overgrowth of bone on the metatarsal head. In addition, there is also deviation of the great toe toward the second toe. In severe cases, the great toe can either lie above or below the second toe. Shoes are often blamed for creating these problems. This, however, is inaccurate. It has been noted that primitive tribes where going barefoot is the norm will also develop bunions. Bunions develop from abnormal foot structure and mechanics (e.g. excessive pronation), which place an undue load on the 1st metatarsal. This leads to stretching of supporting soft tissue structures such as joint capsules and ligaments with the end result being gradual deviation of the 1st metatarsal. As the deformity increases, there is an abnormal pull of certain tendons, which leads to the drifting of the great toe toward the 2nd toe. At this stage, there is also adaptation of the joint itself that occurs.
Symptoms
Red, thickened skin along the inside edge of the big toe. A bony bump at this site. Pain over the joint, which pressure from shoes makes worse. Big toe turned toward the other toes and may cross over the second toe.
Diagnosis
Looking at the problem area on the foot is the best way to discover a bunion. If it has the shape characteristic of a bunion, this is the first hint of a problem. The doctor may also look at the shape of your leg, ankle, and foot while you are standing, and check the range of motion of your toe and joints by asking you to move your toes in different directions A closer examination with weight-bearing X-rays helps your doctor examine the actual bone structure at the joint and see how severe the problem is. A doctor may ask about the types of shoes you wear, sports or activities (e.g., ballet) you participate in, and whether or not you have had a recent injury. This information will help determine your treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment falls into two broad categories, conservative and surgical. From a conservative standpoint, efforts are directed at correcting faulty foot mechanics with custom molded insoles and relief of symptoms. These include Custom Orthosis to stabilize the abnormal motion of the hind and fore foot. Shoe gear modification: Using shoes with larger toe boxed and more supple materials. Changes in activities. Try to avoid those things which cause symptoms. Anti-inflammatory medication for periodic relief this includes cortisone injections into the joint as well as oral medication. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgery isn't recommended unless a bunion causes you frequent pain or interferes with your daily activities. If conservative treatment doesn't provide relief from your symptoms, you may need surgery. There are many different types of surgical procedures for bunions, and no particular bunion procedure is best for every problem. If the bunion gets worse and more painful, surgery to realign the toe and remove the bony bump (bunionectomy) can be effective. Most surgical procedures include a bunionectomy, which involves. Removing the swollen tissue from around your big toe joint. Straightening your big toe by removing part of the bone. Realignment of the 1st metatarsal bone to straighten out the abnormal angle in your big toe joint. Permanently joining the bones the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. It's possible you may be able to walk on your foot immediately after a bunion procedure. However, full recovery can take up to eight weeks or longer with some bunion procedures. To prevent a recurrence, you'll need to wear proper shoes and a foot orthotic after recovery. No surgical procedure is without risk and you may still have pain or you could develop a new bunion in your big toe joint after surgery.
Prevention
A lot of bunion deformities are hereditary so there isn't much you can do to fully prevent them. Early detection and treatment will go a long way in preventing the growth of the bunion and foot pain. Often times, a good custom orthotic can be very effective in slowing the progression of a bunion, but a podiatrist provides that. Waiting with bunions will worsen the condition and could lead to further complications such as hammertoes or contracted toes. Besides causing deformity, these secondary conditions can eventually cause issues with walking and affect your knees, hip, lower back. There are no lotions over the counter that would be able to actually treat the problem. There are some bunion shields that you can place on the bump to ease symptoms and pressure from shoes. However because this condition is an actual bone deformity, the over the counter option solutions are more like a Band-aid approach.
Over-Pronation Of The Feet Causes
Pronation is the normal movement the foot makes to absorb the impact from walking or running. It occurs once the heel strikes the ground and the foot disperses the impact, stretching and flattening the arch as the foot rolls inward. Supination is the opposite motion of pronation. The foot supinates, or rolls on its outer edge, to help with stability as we walk or run. A reasonable amount of pronation is necessary for the foot to function properly. However, when the foot arch remains flat and the foot rolls inward too much one may have excessive pronation or overpronation. This medical condition can result from continually straining the feet and wearing footwear that lacks sufficient foot arch support.

Causes
Unless there is a severe, acute injury, overpronation develops as a gradual biomechanical distortion. Several factors contribute to developing overpronation, including tibialis posterior weakness, ligament weakness, excess weight, pes planus (flat foot), genu valgum (knock knees), subtalar eversion, or other biomechanical distortions in the foot or ankle. Tibialis posterior weakness is one of the primary factors leading to overpronation. Pronation primarily is controlled by the architecture of the foot and eccentric activation of the tibialis posterior. If the tibialis posterior is weak, the muscle cannot adequately slow the natural pronation cycle.
Symptoms
Because pronation is a twisting of the foot, all of the muscles and tendons which run from the leg and ankle into the foot will be twisted. In over-pronation, resulting laxity of the soft tissue structures of the foot and loosened joints cause the bones of the feet shift. When this occurs, the muscles which attach to these bones must also shift, or twist, in order to attach to these bones. The strongest and most important muscles that attach to our foot bones come from our lower leg. So, as these muscles course down the leg and across the ankle, they must twist to maintain their proper attachments in the foot. Injuries due to poor biomechanics and twisting of these muscles due to over-pronation include: shin splints, Achilles Tendonitis, generalized tendonitis, fatigue, muscle aches and pains, cramps, ankle sprains, and loss of muscular efficiency (reducing walking and running speed and endurance). Foot problems due to over-pronation include: bunions, heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, fallen and painful arches, hammer toes, and calluses.
Diagnosis
People who overpronate have flat feet or collapsed arches. You can tell whether you overpronate by wetting your feet and standing on a dry, flat surface. If your footprint looks complete, you probably overpronate. Another way to determine whether you have this condition is to simply look at your feet when you stand. If there is no arch on the innermost part of your sole, and it touches the floor, you likely overpronate. The only way to truly know for sure, however, is to be properly diagnosed by a foot and ankle specialist.
Non Surgical Treatment
No matter what the cause in your case, over pronation can be remedied in several ways. Those who are overweight should consider permanently losing weight to naturally alleviate pressure on the ligaments and heel of the foot. Also, you should consult a podiatrist to examine your posture and movement habits. You may be reinjuring yourself due to poor alignment without even knowing it. If you also have lower back problems, this could be a sign of over pronation as a result of misalignment.
Surgical Treatment
Hyperpronation can only be properly corrected by internally stabilizing the ankle bone on the hindfoot bones. Several options are available. Extra-Osseous TaloTarsal Stabilization (EOTTS) There are two types of EOTTS procedures. Both are minimally invasive with no cutting or screwing into bone, and therefore have relatively short recovery times. Both are fully reversible should complications arise, such as intolerance to the correction or prolonged pain. However, the risks/benefits and potential candidates vary. Subtalar Arthroereisis. An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer. HyProCure Implant. A stent is placed into a naturally occurring space between the ankle bone and the heel bone/midfoot bone. The stent realigns the surfaces of the bones, allowing normal joint function. Generally tolerated in both pediatric and adult patients, with or without adjunct soft tissue procedures. Reported removal rates, published in scientific journals vary from 1%-6%.
Calcaneal Apophysitis In Adolescents
Sever?s Disease is one of the most common overuse sports injuries in the U.S. It may not receive the street cred that plantar fasciitis gets, but this painful condition affecting the heel routinely affects child athletes, usually from eight to thirteen years of age, right when the bones are coming together. The pounding force causes inflammation between the bones, according to YNN, as well as injury to the growth plates themselves. While the ?disease? classification may sound scary, it?s actually a quite normal overuse sports injury that does not typically persist into adulthood.
Causes
During the growth spurt of early puberty, the heel bone (also called the calcaneus) sometimes grows faster than the leg muscles and tendons. This can cause the muscles and tendons to become very tight and overstretched, making the heel less flexible and putting pressure on the growth plate. The Achilles tendon (also called the heel cord) is the strongest tendon that attaches to the growth plate in the heel. Over time, repeated stress (force or pressure) on the already tight Achilles tendon damages the growth plate, causing the swelling, tenderness, and pain of Sever's disease. Such stress commonly results from physical activities and sports that involve running and jumping, especially those that take place on hard surfaces, such as track, basketball, soccer, and gymnastics.
Symptoms
If your child has any of the following symptoms, call your pediatrician for an evaluation. Heel pain that begins after starting a new sports season or a new sport. Walking with a limp or on tiptoes. Pain that increases with running or jumping. Heel tendon that feels tight. Pain when you squeeze the child's heel near the back. Pain in one or both heels.
Diagnosis
This can include physical examination and x-ray evaluation. X-rays may show some increased density or sclerosis of the apophysis (island of bone on the back of the heel). This problem may be on one side or bilateral.
Non Surgical Treatment
The immediate goal of treatment is pain relief. Because symptoms generally worsen with activity, the main treatment for Sever's disease is rest, which helps to relieve pressure on the heel bone, decreasing swelling and reducing pain. As directed by the doctor, a child should cut down on or avoid all activities that cause pain until all symptoms are gone, especially running barefoot or on hard surfaces because hard impact on the feet can worsen pain and inflammation. The child might be able to do things that do not put pressure on the heel, such as swimming and biking, but check with a doctor first.
Surgical Treatment
The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
Foot Arch Pain
Pain or strain in your foot arches is a common sports injury and often linked to inflammation of the plantar fascia, the shock absorption ligament along the bottom of each foot. The pain can also highlight underlying issues to do with the structure of your arches.

Causes
Also known as pes planus, this is when the arch of the foot collapses completely dropping the whole sole of the foot down to the ground. Flat feet are a common cause of foot arch pain. Babies are born with flat feet and as they grow, the foot arches should gradually form, but in approximately 30% of the population, they never do. They can also develop later in life, due to illness, pregnancy, injury, excessive stress on the feet or as part of the aging process. Many people who have flat feet don?t complain of any accompanying symptoms, but some develop foot arch pain, or problems further up the leg such as knee pain or back pain. They may find their feet tire quickly when they are standing or walking, and that it is difficult to rise up onto their tiptoes. Someone who is experiencing pain on the bottom of the foot or elsewhere due to their flat feet can benefit from exercises and orthotics (specially designed insoles to correct the foot position) as well as walking barefoot rather than in shoes. A quick test to see if you have flat feet is to put your foot in a tray of water and then place it on a smooth level surface e.g. thick paper. Have a look at your footprint, the more of the sole of the foot that you can see, the flatter your foot.
Symptoms
Intense heel pain, especially first thing in the morning and after a long day. Difficulty walking or standing for long periods without pain. Generally, the sharp pain associated with plantar fasciitis is localized to the heel, but it can spread forward along the arch of the foot and back into the Achilles tendon. While severe cases can result in chronic pain that lasts all day, the most common flare ups occur first thing in the morning, making those first steps out of bed a form of torture, and in the evening after having spent a day on your feet. Overpronation (a foot that naturally turns too far inward), high arches, and flat feet (fallen arches) can all cause similar arch pain. In these cases, however, the pain is more likely to continue throughout the day rather than being worst in the morning.
Diagnosis
Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
If it is flat feet, then you'd seek professional advice and maybe need orthotics, or arch supports to prevent the pressures and to stop the pain. One of the other reasons you can get pain in this area of the foot is plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a membrane that is inside of the skin and attaches to the heel bone here. It divides into three bands that go out of the foot here: the outer band, the central band, and the medial band here. Often, from impact, you get an inflammation of that attachment to the heel bone and this can often spread up the medial band and this is another way of getting pain in that arch. Now, the way to treat that is also using arch supports but also heel cushions, better soled shoes to prevent the pressure. These things normally disappear after a year, 18 months. Plantar fasciitis is easier to treat because it's not a long term problem. If you do need arch support, something like this would be very good for both problems.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered only after 12 months of aggressive nonsurgical treatment. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the plantar fascia, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite a year of calf stretches. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope, an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Plantar fascia release. If you have a normal range of ankle motion and continued heel pain, your doctor may recommend a partial release procedure. During surgery, the plantar fascia ligament is partially cut to relieve tension in the tissue. If you have a large bone spur, it will be removed, as well. Although the surgery can be performed endoscopically, it is more difficult than with an open incision. In addition, endoscopy has a higher risk of nerve damage. The most common complications of release surgery include incomplete relief of pain and nerve damage. Most patients have good results from surgery. However, because surgery can result in chronic pain and dissatisfaction, it is recommended only after all nonsurgical measures have been exhausted.
Prevention
Stretch and strengthen important muscles in your feet, ankles and legs in order to guard against future strain. Make sure to acquire suitable arch supports and inserts if necessary, and that your shoes are shock absorbent and in good condition. Wearing tattered shoes provides no protection, and runners should replace their footwear before exceeding 500 miles of usage. Athletes new to arch supports should gradually build their training routine, allowing their feet to become accustomed to a new stance.
Stretching Exercises
People with flexible feet who develop fallen arches may benefit from foot strengthening exercises, notes the Nicholas Institute of Sports Medicine and Athletic Trauma. Standing on a towel in bare feet and grasping the material with the toes is an easy foot-strengthening exercise that can be done at home. Standing on one leg while arching and releasing the foot may also prove useful. Doctors may prescribe gentle stretching exercises for the foot and ankle tendons.
What Are The Leading Causes Of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction ?
Overview
Adult-acquired flatfoot or collapsed arch occurs because the large tendon on the inside of the ankle - the posterior tibial tendon - becomes stretched out and no longer supports the foot?s arch. In many cases, the condition worsens and and the tendon thickens, becoming painful, especially during activities. Flatfoot or collapsed arch is also known as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. This condition is different than having flat feet since birth (known as congenital flatfoot), although sometimes these patients develop similar symptoms and require similar treatments. 
Causes
Overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. In fact, the symptoms usually occur after activities that involve the tendon, such as running, walking, hiking, or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch, and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change. For example, when PTTD initially develops, there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon). In addition, the area may be red, warm, and swollen. Later, as the arch begins to flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle. But at this point, the foot and toes begin to turn outward and the ankle rolls inward. As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. The tendon has deteriorated considerably and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Diagnosis
Looking at the patient when they stand will usually demonstrate a flatfoot deformity (marked flattening of the medial longitudinal arch). The front part of the foot (forefoot) is often splayed out to the side. This leads to the presence of a ?too many toes? sign. This sign is present when the toes can be seen from directly behind the patient. The gait is often somewhat flatfooted as the patient has the dysfunctional posterior tibial tendon can no longer stabilize the arch of the foot. The physician?s touch will often demonstrate tenderness and sometimes swelling over the inside of the ankle just below the bony prominence (the medial malleolus). There may also be pain in the outside aspect of the ankle. This pain originates from impingement or compression of two tendons between the outside ankle bone (fibula) and the heel bone (calcaneus) when the patient is standing.
Non surgical Treatment
There are many non-surgical options for the flatfoot. Orthotics, non-custom braces, shoe gear changes and custom braces are all options for treatment. A course of physical therapy may be prescribed if tendon inflammation is part of the problem. Many people are successfully treated with non-surgical alternatives. 
Surgical Treatment
If cast immobilization fails, surgery is the next alternative. Treatment goals include eliminating pain, halting deformity progression and improving mobility. Subtalar Arthroereisis, 15 minute outpatient procedure, may correct flexible flatfoot deformity (hyperpronation). The procedure involves placing an implant under the ankle joint (sinus tarsi) to prevent abnormal motion. Very little recovery time is required and it is completely reversible if necessary. Ask your Dallas foot doctor for more information about this exciting treatment possibility.
Which Are The Main Causes Of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) ?
Overview
Some people have always had flat feet from a young age. Unfortunately as people reach their fifties they will suddenly have one foot with a flatter arch than the other foot. This situation is termed adult acquired flatfoot. Adult acquired flatfoot is a painful condition occurring in one foot. The common patient profile is a female over the age of 50 with pre-existing flatfeet, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and obesity. All of these underlying problems will lead to a weakening of the support structures of the arch. If you have adult acquired flat foot you will not be able to lift your heel off the ground while standing on one leg. Adult acquired flatfoot may develop due to trauma or degeneration of major tendons ankle & foot. Weakness or paralysis of leg muscles can also create a flatfoot deformity. 
Causes
There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. The most common cause of acquired adult flatfoot is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Symptoms
Initially, flatfoot deformity may not present with any symptoms. However, overtime as the tendon continues to function in an abnormal position, people with fallen arches will begin to have throbbing or sharp pain along the inside of the arch. Once the tendon and soft tissue around it elongates, there is no strengthening exercises or mechanism to shorten the tendon back to a normal position. Flatfoot can also occur in one or both feet. If the arch starts to slowly collapse in one foot and not the other, posterior tibial dysfunction (PTTD) is the most likely cause. People with flatfoot may only have pain with certain activities such as running or exercise in the early phase of PTTD. Pain may start from the arch and continue towards the inside part of the foot and ankle where the tendon courses from the leg. Redness, swelling and increased warmth may also occur. Later signs of PTTD include pain on the outside of the foot from the arch collapsing and impinging other joints. Arthritic symptoms such as painful, swollen joints in the foot and ankle may occur later as well due to the increased stress on the joints from working in an abnormal position for a long period of time.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is.
Non surgical Treatment
Nonoperative treatment of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction can be successful with the Arizona AFO brace, particularly when treatment is initiated in the early stages of the disease. This mandates that the orthopedist has a high index of suspicion when evaluating patients to make an accurate diagnosis. Although there is a role for surgical management of acquired flat feet, a well-fitted, custom-molded leather and polypropylene orthosis can be effective at relieving symptoms and either obviating or delaying any surgical intervention. In today's climate of patient satisfaction directed health care, a less invasive treatment modality that relieves pain may prove to be more valuable than similar pain relief that is obtained after surgery. Questions regarding the long-term results of bracing remain unanswered. Future studies are needed to determine if disease progression and arthrosis occur despite symptomatic relief with a brace. Furthermore, age- and disease stage-matched control groups who are randomized to undergo surgery or bracing are necessary to compare these different treatment modalities. 
Surgical Treatment
In cases of PTTD that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required. For some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Surgical treatment may include repairing the tendon, tendon transfers, realigning the bones of the foot, joint fusions, or both. Dr. Piccarelli will determine the best approach for your specific case. A variety of surgical techniques is available to correct flexible flatfoot. Your case may require one procedure or a combination of procedures. All of these surgical techniques are aimed at relieving the symptoms and improving foot function. Among these procedures are tendon transfers or tendon lengthening procedures, realignment of one or more bones, or insertion of implant devices. Whether you have flexible flatfoot or PTTD, to select the procedure or combination of procedures for your particular case, Dr. Piccarelli will take into consideration the extent of your deformity based on the x-ray findings, your age, your activity level, and other factors. The length of the recovery period will vary, depending on the procedure or procedures performed.